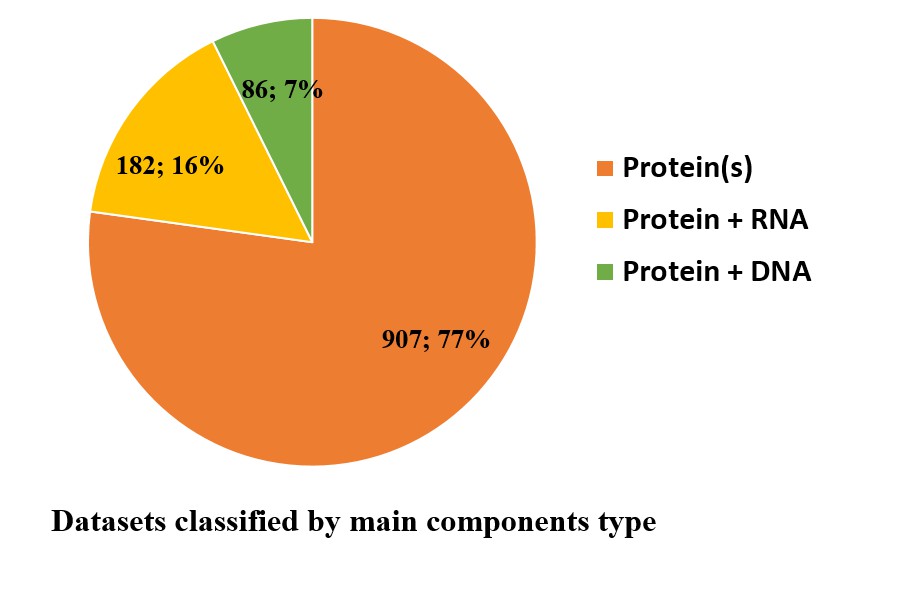
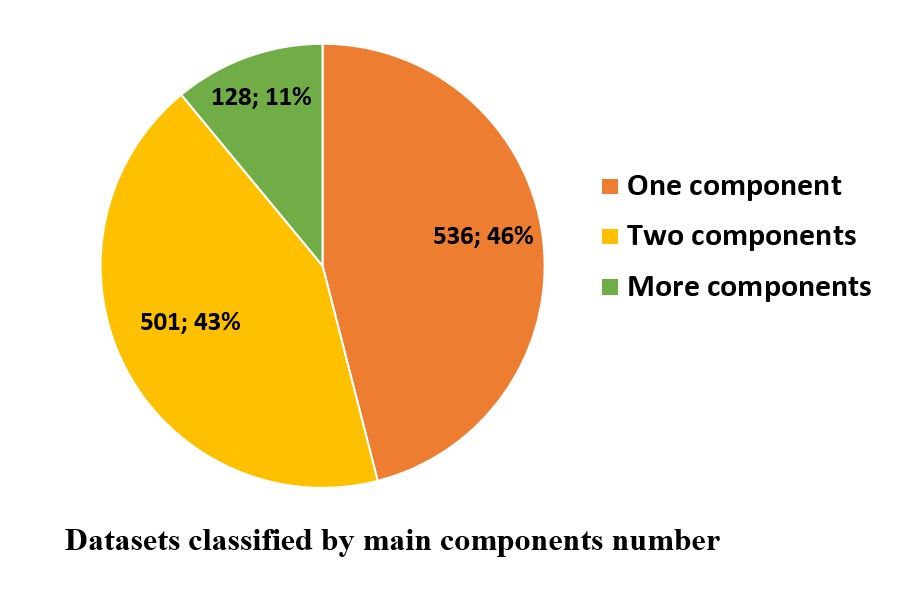
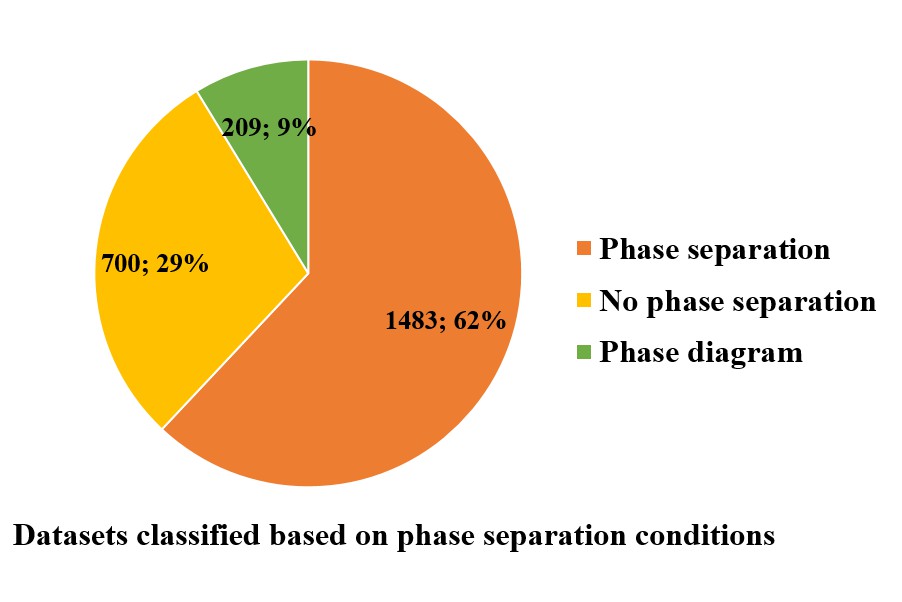
Liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) of proteins has been discovered to underlie the compartmentalization of cells, through the formation of liquid biological condensates including membraneless organelles (MLOs), signaling puncta and so on. LLPS is associated with numerous biological processes such as RNA metabolism, gene regulation and signal transduction. However, the fundamental mechanism of protein LLPS still remains to be elucidated. It is important to systematically analyze all the available experimental data for a better understanding of LLPS. To this end, through extensive literature curation, we summarized the proteins and corresponding experimental conditions under which their phase separation tendencies have been detected in vitro, and deposited them in this database.
LLPSDB contains LLPS related proteins together with the corresponding phase separation conditions validated by experiments. For each protein, the database provides various information, including the protein sequence, modifications on specific amino acids, its ability of coalescing with nucleic acids, biological function etc., as well as specific experimental conditions such as temperature, salt concentration, pH, crowding agent, detected techniques, phase behavior and so on. In addition, several related databases are linked from LLPSDB including Uniprot, MobiDB, DisProt, OMIM, IDEAL, AmyPro, FuzzDB and PubMed. All the data summarized in LLPSDB are available for users.
Q Li, X Peng, Y Li, W Tang, J Zhu, J Huang, Y Qi, Z Zhang, LLPSDB: a database of proteins undergoing liquid–liquid phase separation in vitro.Nucleic Acids Res.,2020: 48(D1):D320–D327 .
- LLPSDB v2.0 was released on Dec 17, 2021. To visit it, please click here
- Access the phase separation protein prediction tool (PSPredictor) based on LLPSDB.
- Correction of several entries was made, and PMID option was added in search module on Sep 19, 2019.
- LLPSDB currently holds 1175 entries. Last updated: July 1, 2019.
Email: biocomp-llpsdb@ucas.ac.cn
Computational Biology Research Group,
College of Life Sciences,
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Beijing, P.R.China, 100049